Course: Advanced Distributed System Design - Udi Dahan
Coupling

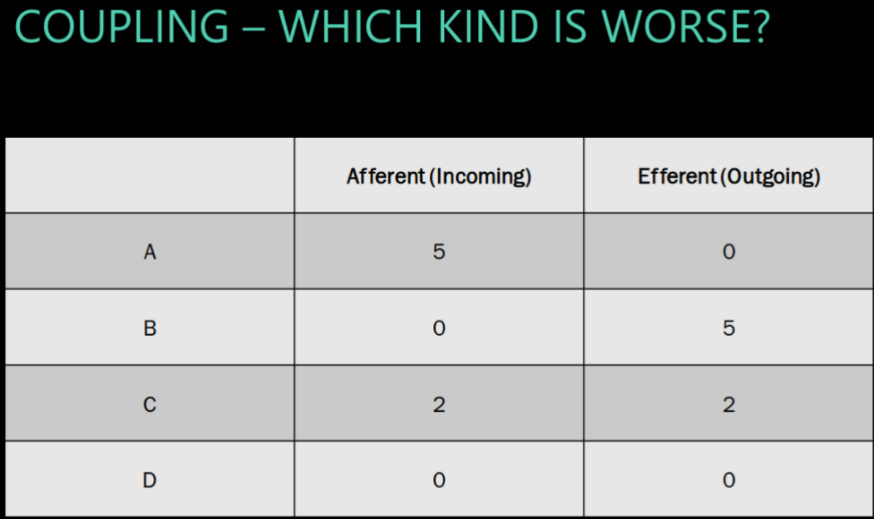
incoming vs outgoing coupling
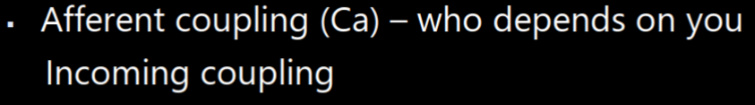
def: incoming coupling
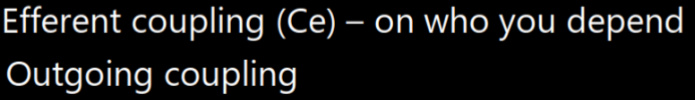
def: outgoing coupling
clarity: incoming vs outgoing

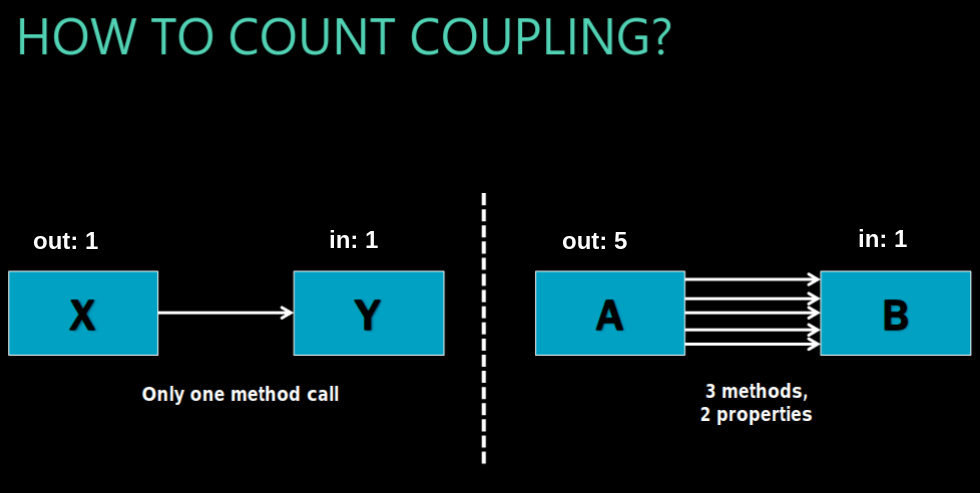
count coupling X->Y x outboing 1 y incoming 1
A->B x outgoing 5 “is this class single responsibility principle” y incoming 1 “how many classes do I have to change”
static analysis tool
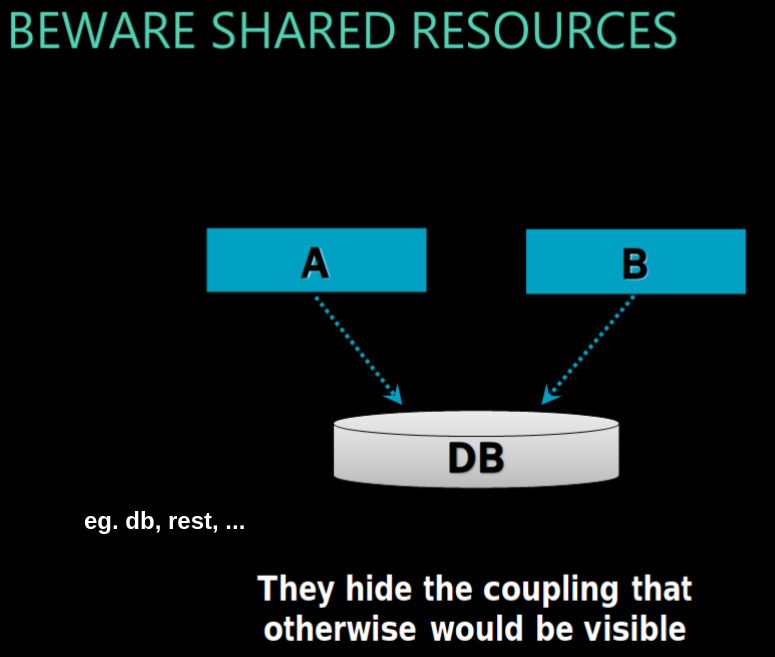
hidden coupling
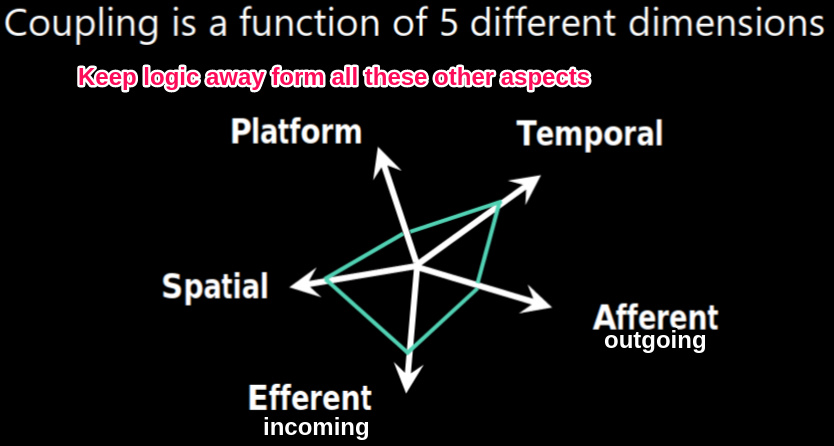
3 aspects of coupling

aspect 1: platform (aka interoperability)

text-based representation on the wire http, smtp, udp, …
soap / wsdl / rest
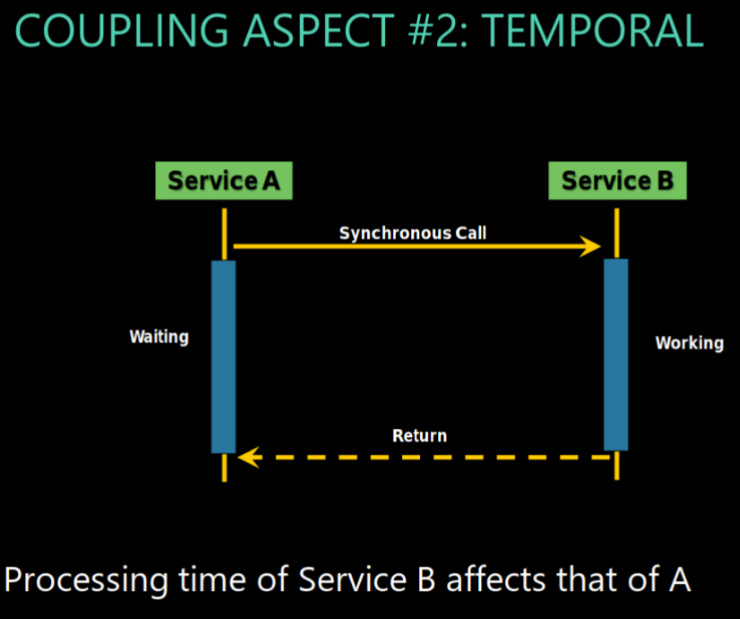
apect 2: time
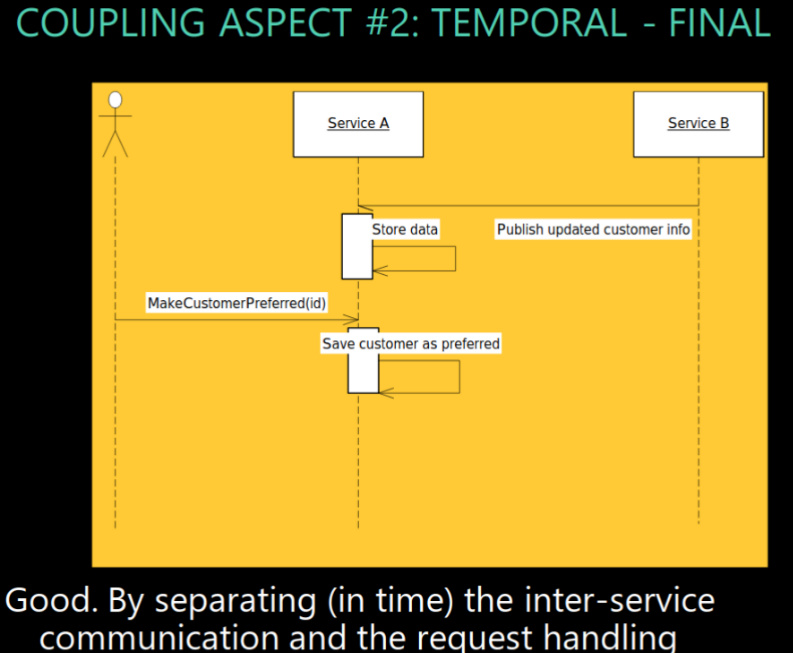
aspect time: Pub-Sub explicit caching
make explicit in A that caching is happening
aspect time: Pub-Sub constraints

aspect time: Pub-Sub add validity period to data

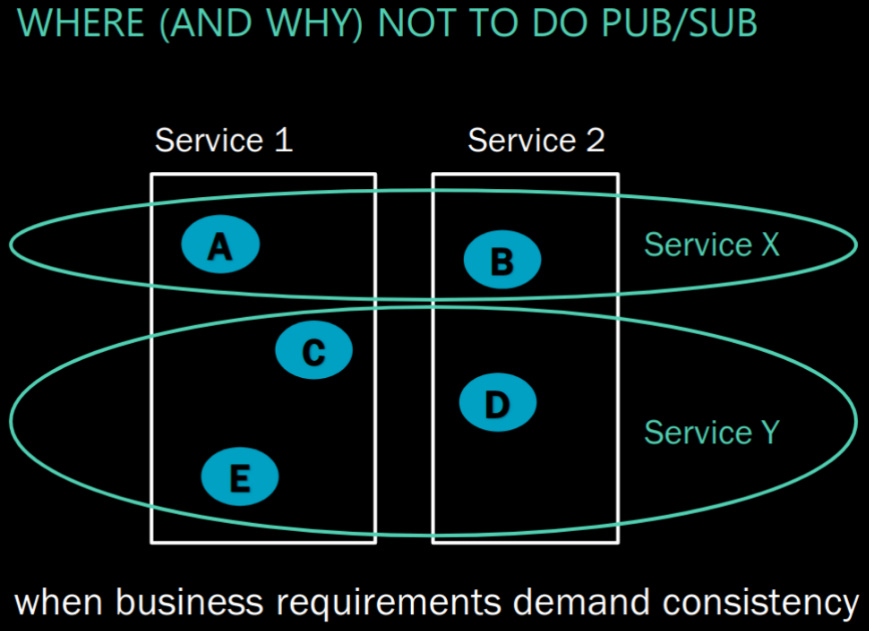
aspect time: Pub-Sub consitency
if pub sub not OK time-constraint, then RPC also not OK (can use cache) -> transaction across A and B needed
aspect space: routing

aspect time: logical owner logical owner

coupling 5 dimensions tradeoffs tradeoffs between dimensions per ‘’layer" keep LOGIC away from all the other “is the coupling reasonable for it’s responsibility” eg. fromend webapi, platform low, even if HTTP response which is time high coupling internal component: low temporal at cost of higher platform (pub-sub platform framework)