Model: Data ownership (in microservice architecture)
the owner is the one who writes to the table
(1) Pattern: Single Ownership (2) Pattern: Common Ownership
- solution: create a service around the shared table
(3) Pattern: Joint Ownership
- solution 1: table split pattern
- solution 2: data domain
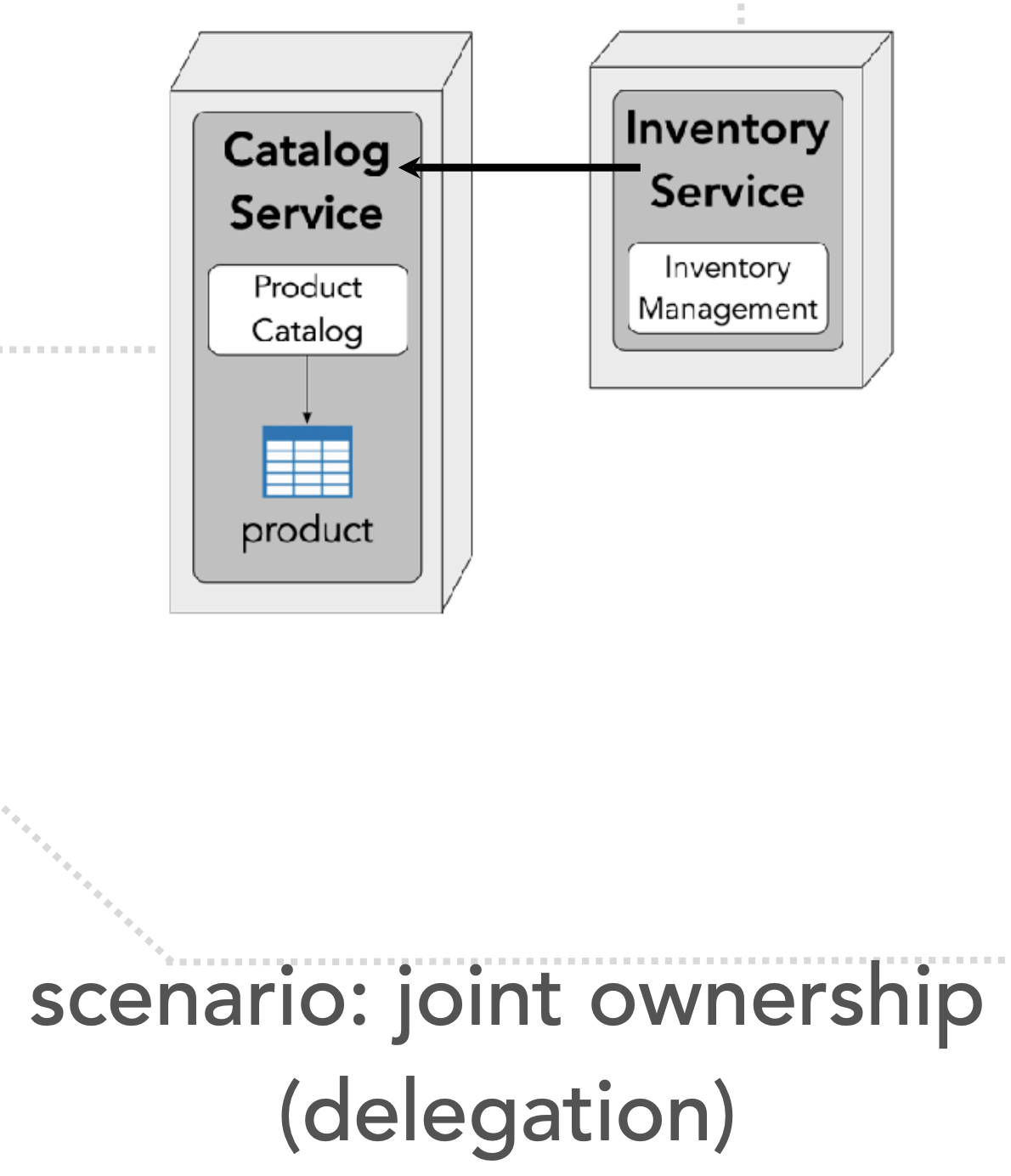
- solution 3: delegation
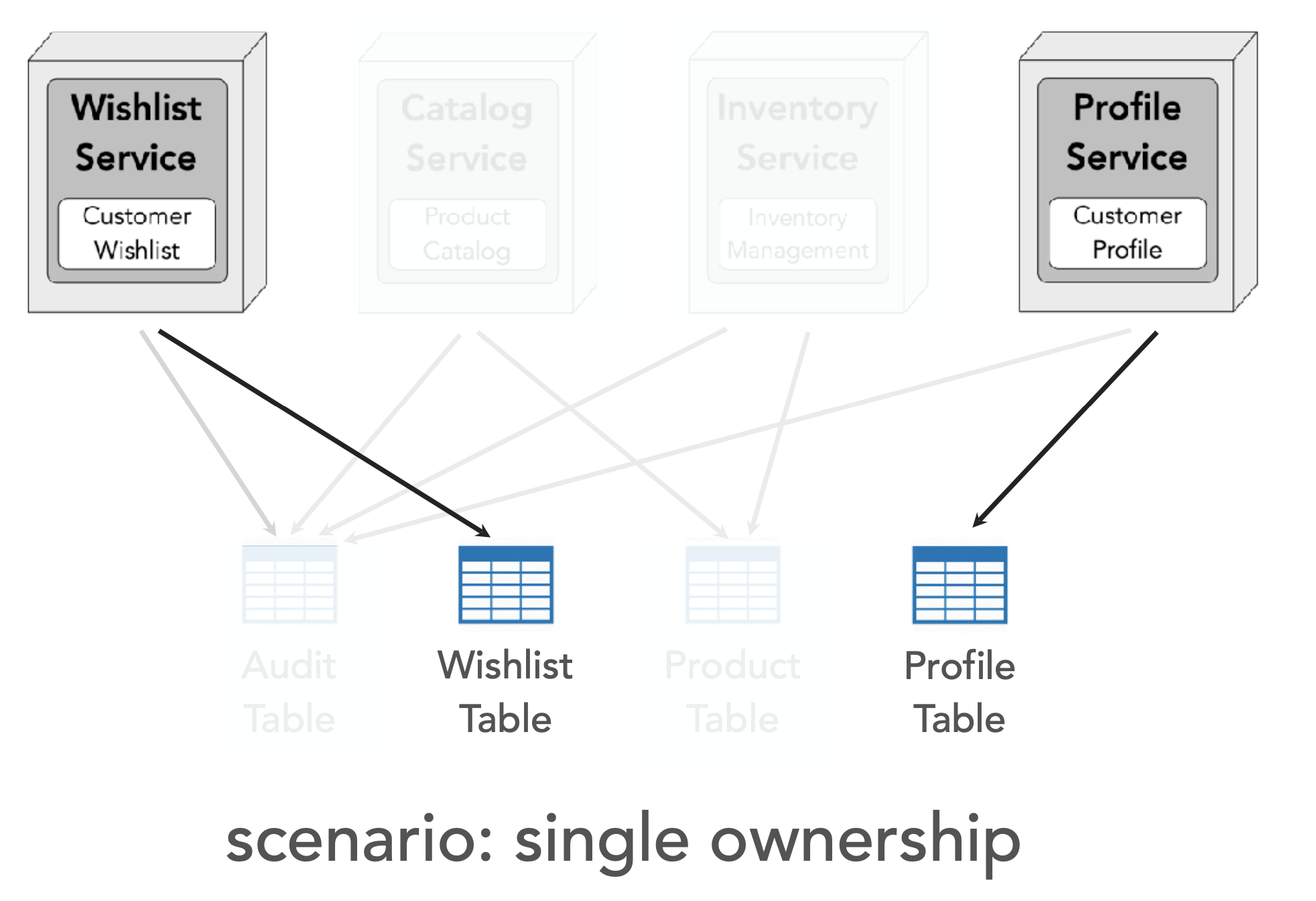
(1) Pattern: Single ownership (data ownership in microservices)
(2) Pattern: Common Ownership (data ownership in microservices)
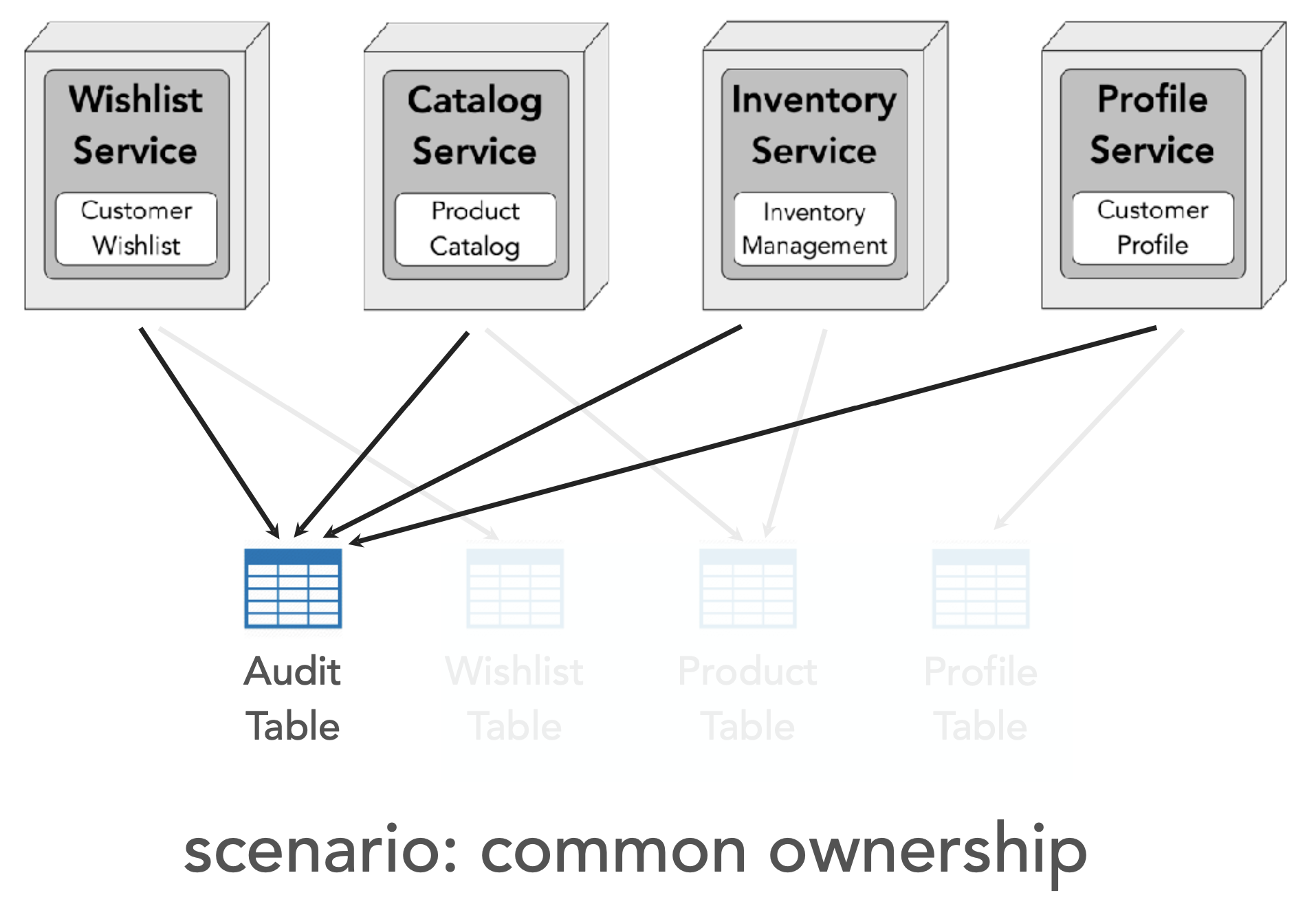 solution: create a service around the shared table
eg. create a service “Audit Service”
solution: create a service around the shared table
eg. create a service “Audit Service”
(3) Pattern: Joint Ownership (data ownership in microservices)
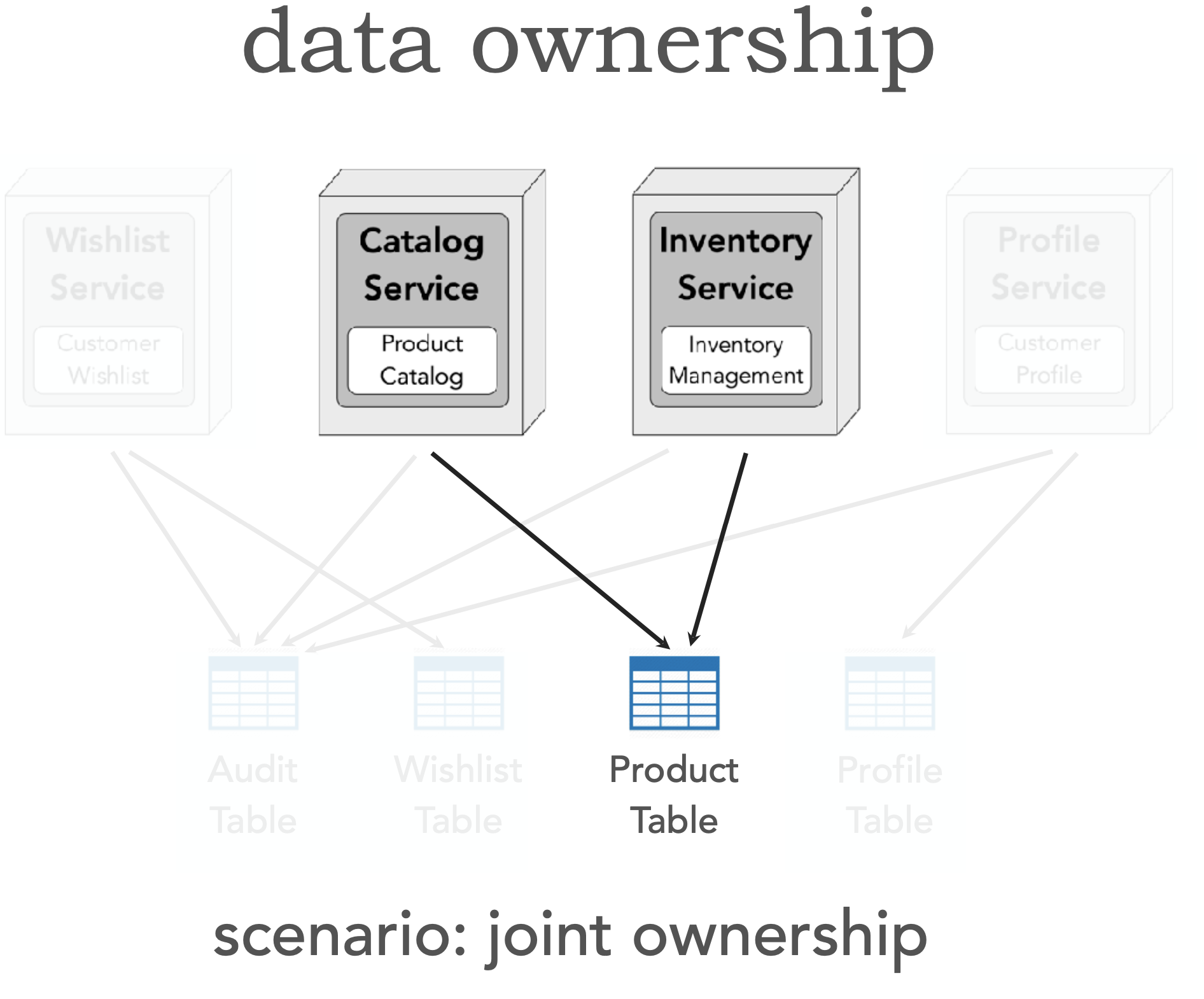
Solution 1: table split pattern
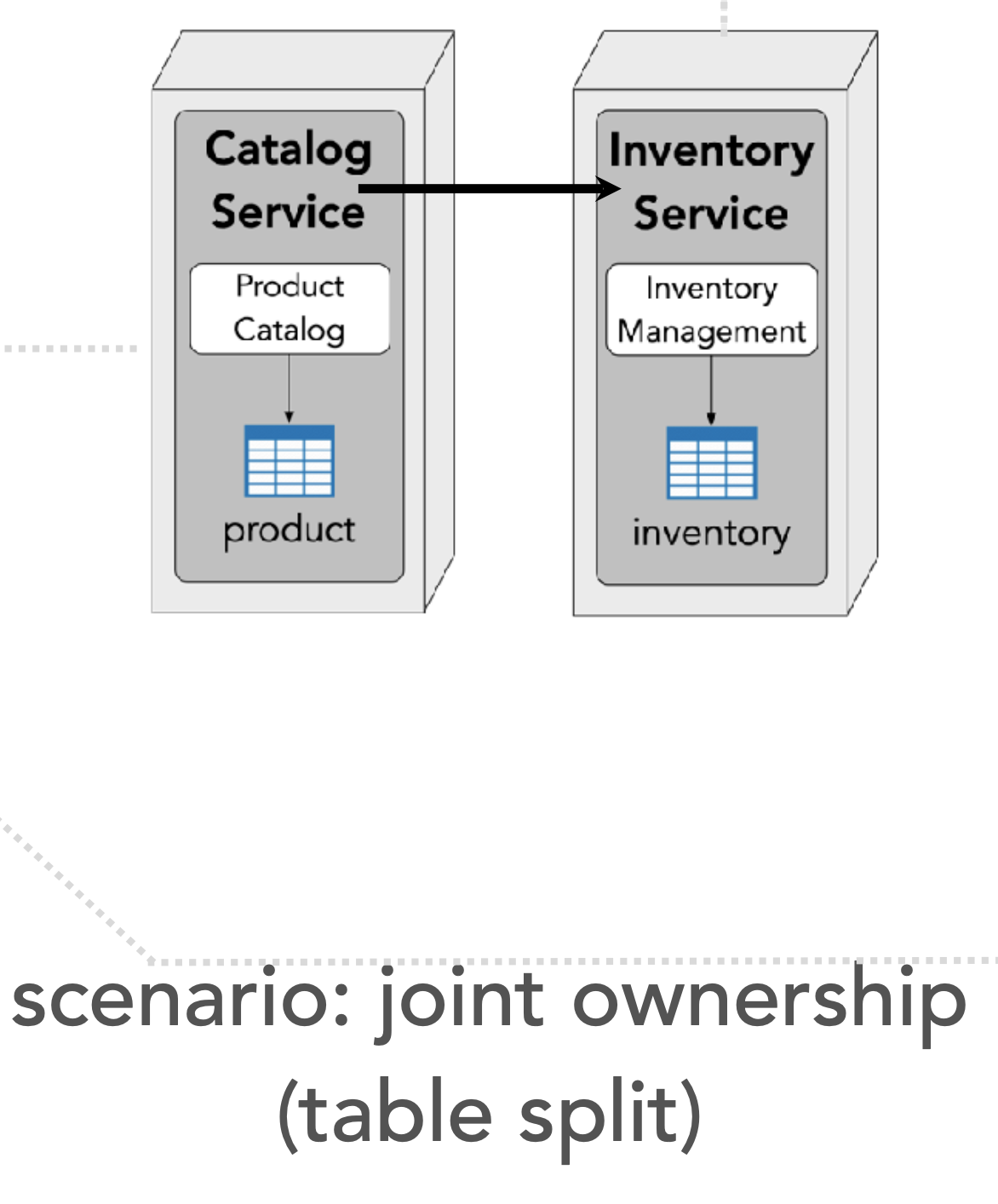 catalog needs to update inventory
synchronous vs asynchronous communication
catalog needs to update inventory
synchronous vs asynchronous communication
Solution 2: data domain
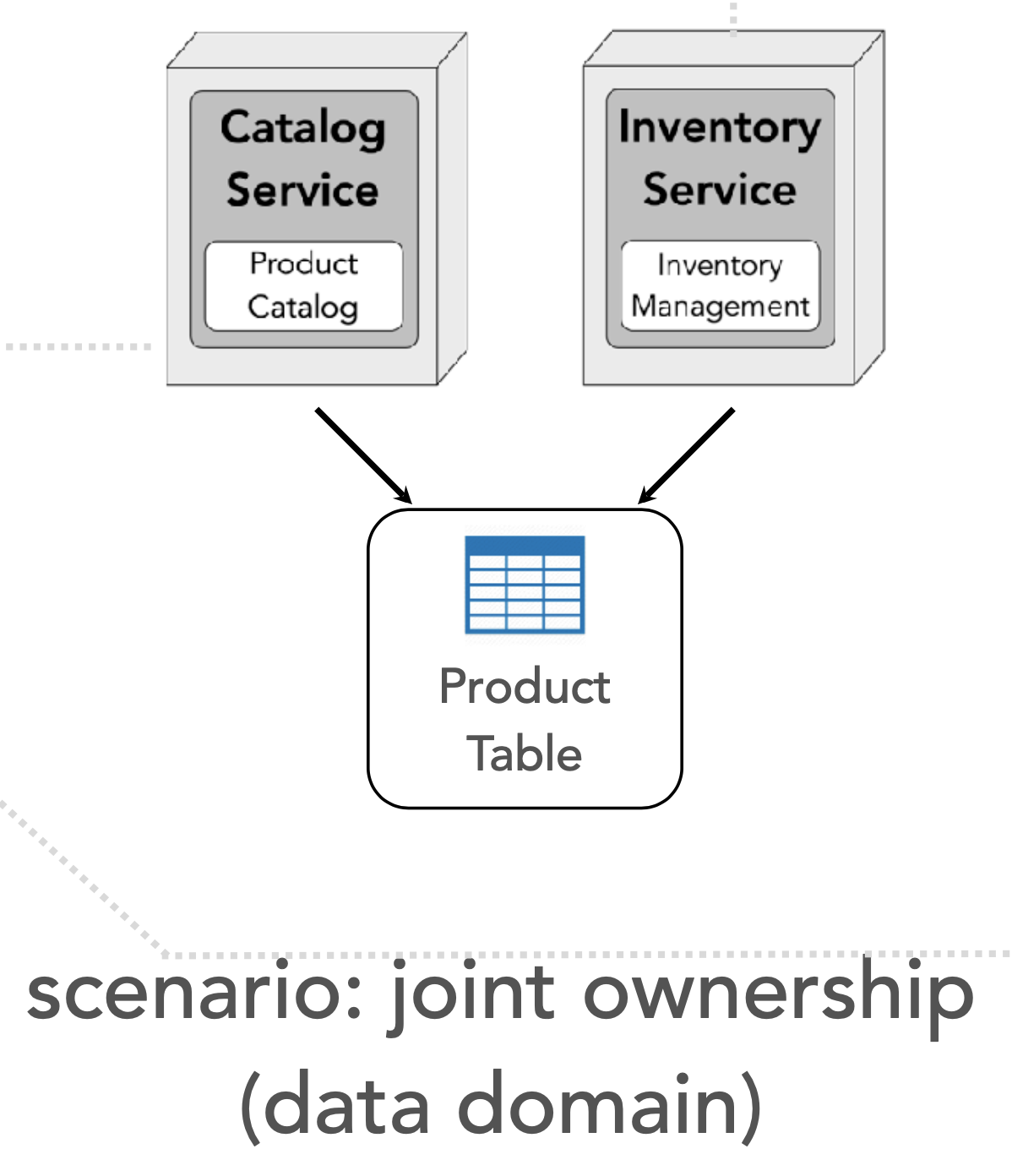 -> bounded context now contains 2 services
-> bounded context now contains 2 services
Solution 3: delegation